
The revised legal framework from the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights includes new standards on gender-based violence and online communication. In an interview with LJR, the Special Rapporteur for Freedom of Expression warns of rising legal harassment and urges governments to prioritize online literacy as a tool for protecting free speech.

Three years after Dom Phillips was killed alongside Indigenous rights expert Bruno Pereira, fellow journalists completed his final work. He sought to answer how to save the world’s largest rainforest — and why.

Claudia Duque has spent two decades fighting for justice after being spied on and threatened by government agents. So now that the state is finally offering an apology, why is she refusing to accept it?

El Faro, the leading investigative outlet in El Salvador, says the government is preparing arrest warrants against its journalists following publication of interviews linking President Nayib Bukele’s political rise to support from gangs.

A new Reporters Without Borders report finds economic instability hurt the media industry in most Latin American countries last year. Nicaragua, under an increasingly repressive dictatorship, overtook Cuba as the region’s worst country for press freedom.

Scholars warn that press freedom in Latin America is threatened not only by dictatorships but also by democratic governments and media capture. At the Iberoamerican Colloquium on Digital Journalism, they called for innovative, collaborative responses.

As systematic persecution by the Ortega-Murillo regime forces entire newsrooms to flee, exile has become a defining feature of Nicaraguan journalism. At the Ibero-American Colloquium on Digital Journalism, reporters shared their efforts to report, resist and stay safe.

Clarice Herzog, 83, fought for decades to prove her husband was murdered under Brazil’s dictatorship. But his killers remain unpunished.
“Crime without punishment: how the military killed Rubens Paiva" is the result of years of research and journalistic investigation, reconstructing the events that led to Paiva's death. Dal Piva defends the importance of memory and journalistic investigation for understanding this dark period in Brazilian history.

The analysis of public advertising in 11 countries across the region shows how governments misuse funds, rewarding loyalists and endangering independent news outlets.
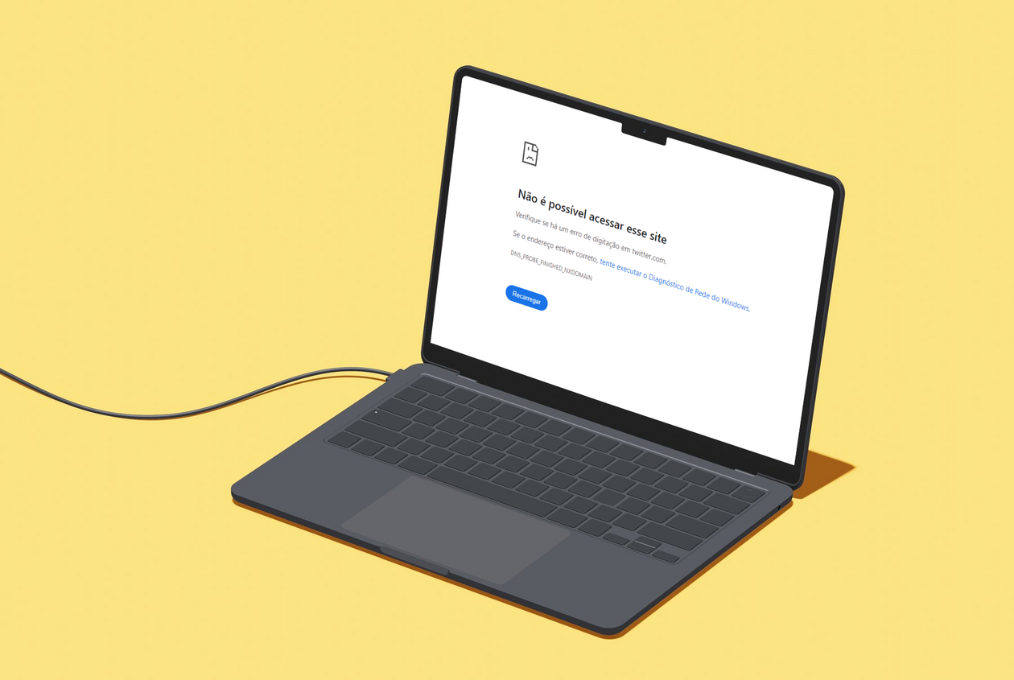
We talked to some of Brazil’s top journalists about the ban on X. Many are relieved, but one reports: “There's a gap in coverage that I don't know how to fill.”

In the book “Historia del Periodismo en Chile. De La Aurora a las Redes Sociales” ("History of journalism in Chile: from La Aurora to social media"), author Alfredo Sepúlveda explains over more than 500 pages how tensions between media, journalists and political power permeate the entire history of journalism in the country.