Artificial intelligence continues on an increasingly fast path to becoming entrenched in many industries, including journalism. In newsrooms, this technology is transforming tasks that were previously performed by humans, such as news writing, image generation and data analysis.
The report “Journalism, media, and technology trends and predictions 2024,” published in January by the Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism, said that this would be the year for AI to be fully incorporated in newsroom workflows. Of media outlets around the world surveyed for the report, 16% reported having already appointed a person responsible for AI-related activities in their newsrooms, while 24% said they plan to do so soon.
However, journalist and researcher Nic Newman, author of the report, said that Latin American editors have taken longer to adapt to the arrival of AI in journalism, and are consequently less prepared to face this technological disruption.
For that reason, below we present a list of 15 key concepts that every journalist should know in order to navigate confidently through this transition of journalism towards the era of AI.
Each term is accompanied by a specific and real case of its use in newsrooms, as a way to show the effects that this technology is having on the industry.
Abbreviated as AI, artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science that focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks that would normally require human intelligence. AI systems have the ability to perform complex functions and solve complex problems in less time than it would take humans.
In the journalistic context, AI can be applied for tasks such as process automation, data analysis, identification of patterns and trends, and automated content generation, among others.
Example in journalism: Heliograf, the “journalist robot,” has been one of The Washington Post's big bets on the application of AI to position itself as a newspaper at the forefront. Developed to automate the writing of articles involving large amounts of data, Heliograf debuted in the newspaper's coverage of the Rio de Janeiro Olympic Games in 2016, and that same year it was used to generate articles, newsletters and social media posts around presidential elections in the United States.
An algorithm is an ordered sequence of pre-established instructions that a machine or system follows to solve a problem or execute a specific task. Algorithms work from data provided by human beings, which they process and then deliver a result.
Example in journalism: In 2018, Peruvian investigative journalism outlet Ojo Público premiered “Funes,” which it called “the algorithm against corruption.” It uses risk indicators to detect possible corruption in public procurement. The tool analyzed nearly 245,000 public contracts from various public institutions in Peru and, based on the results, Ojo Público was able to reveal potential cases of corruption, money laundering and hidden relationships between companies and governments in several journalistic investigations.
Machine learning is a subarea of AI in which machines progressively “learn” from experience and based on data provided by human beings.
Machine learning allows tasks such as predictive analysis, pattern recognition, personalization and process optimization to be executed with high precision, thanks to algorithms that “learn” to analyze large volumes of data.
Example in journalism: Perspective, a tool developed by Spanish newspaper El País in collaboration with Google, uses machine learning models to identify inappropriate messages in the comments area of the newspaper's website. The tool works from a database of comments labeled by humans as toxic. Perspective analyzes those thousands of comments and “learns” to identify patterns of toxicity. With this learning, the tool is able to identify comments that have similarities with those in its database and labels them as harmful or inappropriate.
Neural networks are machine learning models inspired by the structure and functioning of the biological brain. They are made up of interconnected units called "artificial neurons" that process information and learn from data. Neural networks create an adaptive system that machines use to learn from their mistakes and continually improve.

Quispe Chequea, of the Peruvian media outlet Ojo Público, uses generative AI resources to produce text and audio content in indigenous languages. (Photo: Screenshot from Ojo Público's website)
Neural networks are the fundamental unit of LLMs due to their unique ability to learn complex patterns in large amounts of data. This makes LLMs capable of executing tasks such as coherent text generation, natural language understanding or sentiment analysis.
Example in journalism: The Argentine media company Grupo Octubre developed Visión Latina in 2022. It’s an AI tool to catalog and identify Latin American characters in its audiovisual material. The tool works from AI recognition models that are capable of learning to identify patterns thanks to a neural network that extracts characteristics from images, such as edges, textures, shapes, colors, etc.
Visión Latina was trained with a database created by Grupo Octubre with images of main figures of Latin American politics and culture, so that the AI recognition model learned to identify them for subsequent searches.
Deep learning is a type of machine learning in which machines are capable of “learning” from experience without human intervention. Deep learning involves artificial neural networks and several layers of information processing, which makes it possible to understand complex patterns in large volumes of data.
Deep learning is particularly useful in processing unstructured data, such as images, audio or video. Some of the tasks where this type of machine learning can be applied include text analysis, automatic content generation, speech recognition, image analysis, and pattern detection.
Example in journalism: MIT researchers developed a deep learning model to detect false news. The model is capable of identifying linguistic patterns of false news and of real information. According to MIT, the model was trained with a set of around 12,000 false news articles from 244 different websites, and with a set of more than 10,000 real news articles from outlets such as The New York Times and The Guardian. When analyzing an article, the model scans the text and looks for patterns similar to those learned and sends them to a series of processing layers until it determines whether the text is more or less likely to be false.
Generative AI is the type of artificial intelligence capable of creating new content by learning from existing massive data. Generative AI models learn patterns from large volumes of data and then generate content that follows those patterns, whether in text, image, sound or video format.
Current generative AI models have been trained with massive amounts of online information from sources such as news articles, books, web pages, open databases, among others. This diversity of sources allows the models to learn linguistic patterns, grammatical structures and semantic relationships to apply them in the generation of new content.
Example in journalism: In 2023, Peruvian investigative outlet Ojo Público developed Quispe Chequea, a tool that uses generative AI resources to produce fact-checked content in text and audio in Indigenous languages. First, the tool generates text in the format of a fact check from pieces of information previously verified by journalists. Subsequently, based on this text,Quispe Chequea generates audio in Spanish or in the Indigenous languages Quechua, Aymara and Awajún.
This is a branch of AI focused on the interaction between computer systems and human language. NLP aims to make machines capable of understanding, interpreting and generating language in a way similar to humans.
Some of the tasks that use NLP are automated translation, generating text or audio content, and answering questions.
Large language models (LLMs) are AI models that have been trained using enormous amounts of text. These models use NLP and machine learning to understand and generate a natural language that emulates how humans speak or write.
An LLM is capable of performing tasks such as writing texts, translating, summarizing documents, conversations, among others.
Example in journalism: Argentine data verification outlet Chequeado carried out an experiment in 2024 as part of its Artificial Intelligence Laboratory through which it tested three large language models to determine which was the most efficient for generating threads on the social network X. The media outlet gave the LLM an article from its website as a basis. From there, the models had to create a thread respecting the main points and style of the article.
Chatbots are AI programs designed to hold conversations with human users. These systems use NLP techniques to understand and respond to user input by emulating human communication.
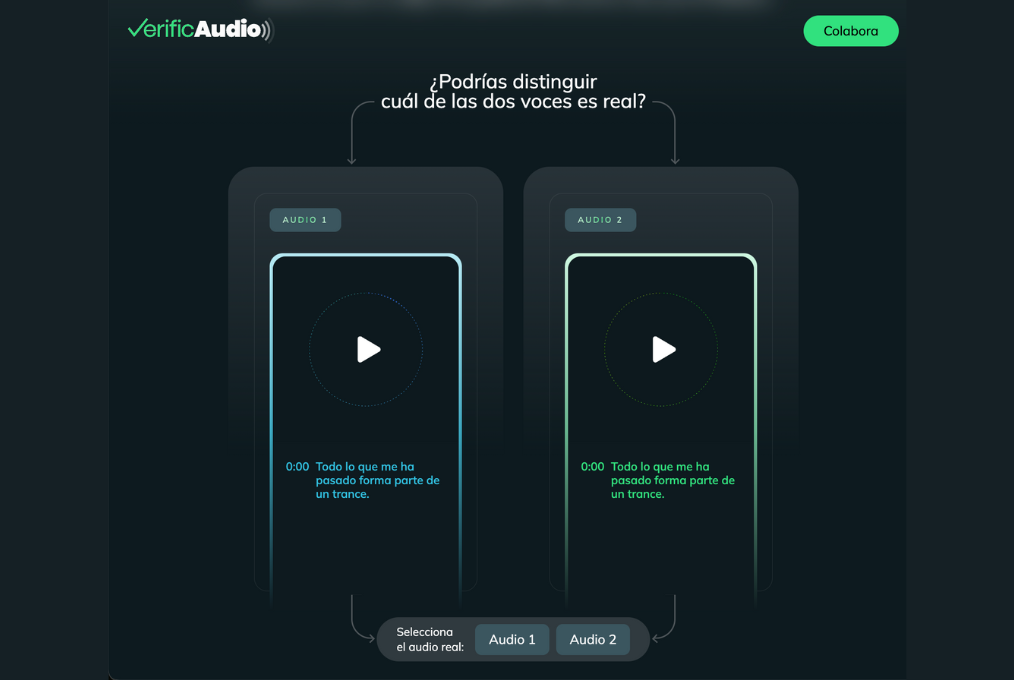
VerificAudio, from the PRISA media group, uses PLN models to analyze pieces of audio and help detect deepfakes. (Photo: Screenshot from the VerificAudio website)
There are basic chatbots that simply follow predefined rules to answer specific questions, but there are also more complex ones that use machine learning to improve their answers with experience. Some of the most advanced chatbots use LLM to generate much more elaborate responses with contextual references.
Example in journalism: In 2018, Brazilian fact-checking organization Aos Fatos launched Fátima, a chatbot to help readers verify information through a conversation on WhatsApp, Telegram, Twitter and Facebook Messenger. In 2023, Aos Fatos launched the FátimaGPT version, which incorporates LLM technology to interpret user questions and offer more relevant answers in natural language.
Unlike its first version, which worked solely by comparing user questions with Aos Fatos files, FátimaGPT is connected to a generative AI model, making the chatbot capable of responding to complex topics with more nuance and context.
GPT (generative pre-trained transformer) models are a type of LLM developed by the organization OpenAI. They are based on the architecture of transformers, which are deep learning models capable of “understanding” the context of the information in a deeper way by transforming words into numerical representations called vectors, which allow them to identify the semantic and syntactic relationships of the language.
Transforming information into vectors allows GPT models to perform tasks as complex as generating human-like language. These models are the engine of ChatGPT, OpenAI's generative AI chatbot.
Example in journalism: Agência Tatu, a media outlet that specializes in data journalism in Brazil, launched SururuBot in 2023. It’s a generative AI tool that produces weekly texts about job vacancies in the city of Maceió. SururuBot works with the GPT-3.5 model, which enables the generation of text based on data about available job offers.
In the context of generative AI, a prompt is an initial instruction or question given to a system to generate a response or perform a specific task. Experts say that the clearer and more specific the prompts are, the more precise the responses from AI platforms will be.
Example in journalism: Northwestern University AI and journalism experts Mowafak Allaham, Michael Crystal, Mona Gomaa and Nicholas Diakopoulos developed a guide on prompting techniques and best practices for journalists. They describe different techniques for using a generative AI tool to obtain the most accurate results possible for journalistic tasks. The guide includes illustrative examples in news production, as well as a resource list with other guides and manuals for specializing in creating prompts in newsrooms.
An API (Application Programming Interface) is an interface that allows one application or computer system to communicate with another to take advantage of its capabilities. In essence, an API is a bridge that allows one software to access the functions or data of another software.
In the context of AI, an API allows developers to integrate AI capabilities within their own applications without needing to develop those capabilities from scratch.
Example in journalism: Botalite is a business solution provider (BSP) of the Spanish fact-checking organization Maldita.es that is authorized by the technology company Meta to access the WhatsApp API. With this, Botalite can develop products and services linked to the functions and features of the messaging platform.
Thanks to this, journalism organizations that work with Botalite, such as Chequeado (Argentina), La Silla Vacía (Colombia) and Documented (United States), have been able to develop tools, mainly chatbots, without having to create them from scratch.
Fine-tuning is a technique within AI that consists of modifying a previously trained model to adapt it to a new task or a specific data set. Instead of starting model training from scratch, which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming, you use an already trained model and fine-tune it with a smaller, more specific data set for the task at hand.
Example in journalism: In 2023, Colombian investigative media outlet Cuestión Pública developed AI tool Odin to generate journalistic content taking advantage of the media outlet’s investigations archive. It was important to the media outlet that the content generated by Odin had its characteristic tone and style. To do this, they customized OpenAI's GPT 3.5 model through a fine-tuning process, based on a set of Cuestión Pública’s threads on X. In this way, the model was retrained to learn to write with the tone and style of those threads.
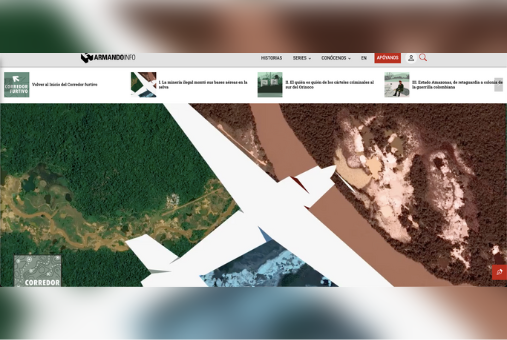
For the “Corredor Furtivo” series, Armando.info used a computer vision algorithm to detect tracks and illegal mines in satellite images. (Photo: Screenshot from Armando.info website)
Also known as opinion mining, sentiment analysis is an AI technique for identifying emotions in text. Sentiment analysis systems use NLP algorithms to analyze words, phrases and contexts within the text to determine, for example, whether the sentiment expressed is positive, negative or neutral.
Example in journalism: “Attack Detector” is an AI tool to detect hate speech against journalists on Twitter. It was developed by the Brazilian Association of Investigative Journalism (Abraji) and the Mexican data journalism organization Data Crítica. One of the NLP models with which “Attack Detector” works is RoBERTa, a sentiment analysis model developed by Meta capable of identifying the emotional tone in a text, in this case, hate.
Computer vision is a technology that allows machines to extract, process and analyze information contained in visual data, such as images and videos. This includes detecting objects, recognizing faces and analyzing movements, among other tasks.
Not all computer vision systems use AI. However, those that apply AI techniques, such as machine learning or deep learning, are capable of performing more sophisticated functions, such as recognizing complex patterns in images, and AI improves their accuracy and effectiveness.