For Borja Echevarria, vice president and digital editor-in-chief at Univision, the way forward at the legacy media company involves collaboration and diversity.
Brazilian fact-checking startup Aos Fatos (translated as To the Facts) is celebrating its one-year anniversary and already making plans to expand its digital presence and to invest in publishing via video. Created in July 2015, the organization is dedicated to verifying facts and statements made by authorities, a journalistic practice that has become known as fact-checking.
Latin American journalists and editors gathered in Buenos Aires, Argentina earlier this month to share experiences and successful methods for producing a kind of investigative journalism that has been growing in the region: fact-checking.
The Panama Papers, the biggest leak in journalism’s history, led to a global investigative effort joined by about 100 Latin American journalists who were able to untangle how fiscal paradises work. Under the leadership of Spanish journalist Mar Cabra, the global data team from the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ) was the brain behind the investigation that required an analysis of 11.5 million documents; the team proved that knowing how to deal with big data has become essential to investigative journalism.
The number of fact-checking journalistic projects around the world has almost doubled between 2015 and 2016, according to an annual census of the Duke Reporters' Lab. According to the study, there are now 96 active fact-checking projects in 37 countries - in 2015, there were 64 projects, and 44 the previous year.
In a saturated and rapidly evolving digital media landscape, discerning truth from fallacy has proven to be a challenge for readers, especially in the case of government discourse. In response to a growing demand for trustworthy and accurate news, the practice of fact-checking has emerged as a practice that allows journalists to hold public officials accountable for their statements.
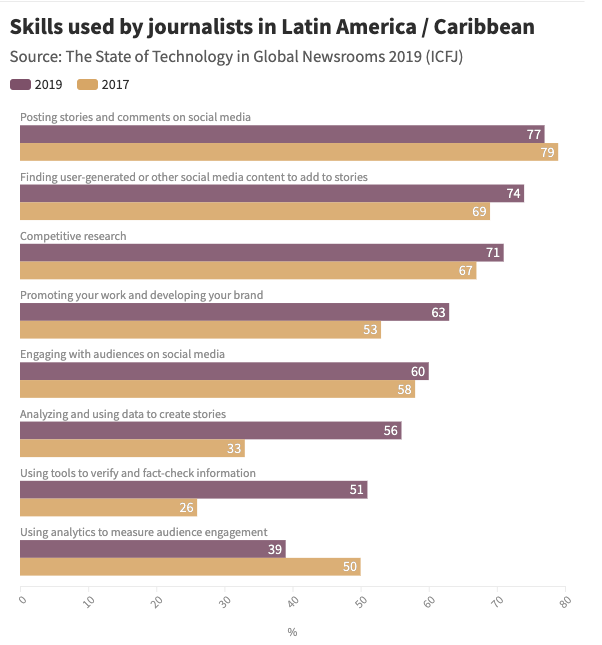
In 2017, 51 percent of journalists from around the world who took part in the survey said they used digital fact-checking and information verification tools, while only 26 percent of Latin American journalists said the same.

The current pandemic highlights the need for journalists to work together as the coronavirus, as well as disinformation surrounding it, crosses languages and borders.

Comprova, a Brazilian collaborative project that brings together 24 media outlets in the country, started what it calls a special phase to verify information about the new coronavirus.
A global collaboration project between fact-checking organizations is working to disprove rumors and combat disinformation about the Sars-CoV-2 coronavirus epidemic.

Election coverage is perhaps one of the biggest challenges in newsrooms: processing large volumes of information in a short time and with the same team that works in everyday conditions.

Diferentemente de outros países latino-americanos, a Colômbia não tem eleições presidenciais neste ano, mas elegerá representantes locais como governadores, prefeitos e vereadores, entre outros cargos, em 27 de outubro. Como nas eleições presidenciais, as campanhas regionais podem ser afetadas pela disseminação de informações falsas.