
It is the potential development of this expertise that attracted the venture capitalists, aiming to open new markets and replicate the model in other countries.

The CEO of Plop Contenido believes that Ampli is still in an experimental stage, in which he wants to test the premise that it is possible to produce news content with a humorous footprint.
According to Pires, there are many reasons for Google to care about and invest in strengthening journalism globally.

When we are talking about artificial intelligence in journalism, we need to talk about the human-centered aspect, said Nick Diakopoulos, assistant professor in Communication Studies and Computer Science at Northwestern University on April 13 at the 20th annual International Symposium on Online Journalism (ISOJ).

Eleven media outlets from Latin America worked on the latest transnational investigation spearheaded by the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ).

Instruction on entrepreneurial journalism is present in just 2.8 percent of universities and journalism schools in Latin America, while that same figure is 20 percent in Spain.

A crowdfunding platform that has become one of the most successful in Brazil with projects ranging from comics and board games to films, music albums and theater shows is creating a project dedicated solely to independent journalism.

With little more than 80,000 inhabitants in Peru and part of Brazil, the Asháninka are the most numerous ethnic group in the Peruvian Amazon. The National Institute of Radio and Television of Peru (IRTP, for its initials in Spanish) recently launched "Ashi Añane", an informative program in the Asháninka language, to give the culture a national platform.

Members of the growing data journalism community in Brazil gathered from Nov. 10 to 11 for the third edition of the Brazilian Conference on Data Journalism and Digital Methods, Coda.Br, in São Paulo.

From the Brazilian Euclides da Cunha to Peruvian Gabriela Wiener, to Colombian Gabriel García Márquez, Argentinean Leila Guerriero, Mexican Alma Guillermoprieto and dozens of other names, Latin America is home to great tellers of real stories that bring elements of literature to journalistic texts.

The Guatemalan investigative journalism site Plaza Pública recently launched a journalism and safety protocols manual for journalists that summarizes the lessons of its first six years of existence.
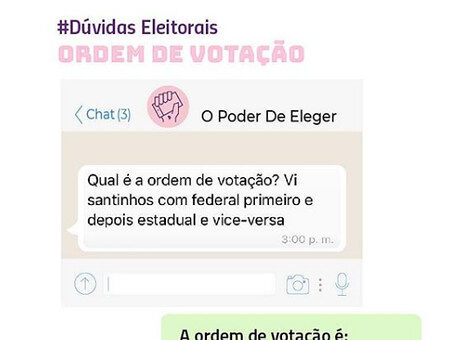
WhatsApp has 120 million active users in Brazil, according to what the company reported in July this year. This number is equivalent to more than half of the Brazilian population, estimated at 208.5 million people.