
In Venezuela, digital information freedoms are systematically censored and attacked, according to “Algorithms of Silence,” the 2023 Digital Rights Report from IPYS Venezuela. During the past year, 46 informative sites were blocked and 12 media outlets and four journalists suffered from identity impersonation.

Venezuelan journalists and photojournalists do other jobs outside of journalism to have extra income that allows them to survive. In 20 years of the governments of Hugo Chávez and Nicolás Maduro, 400 media outlets have closed.
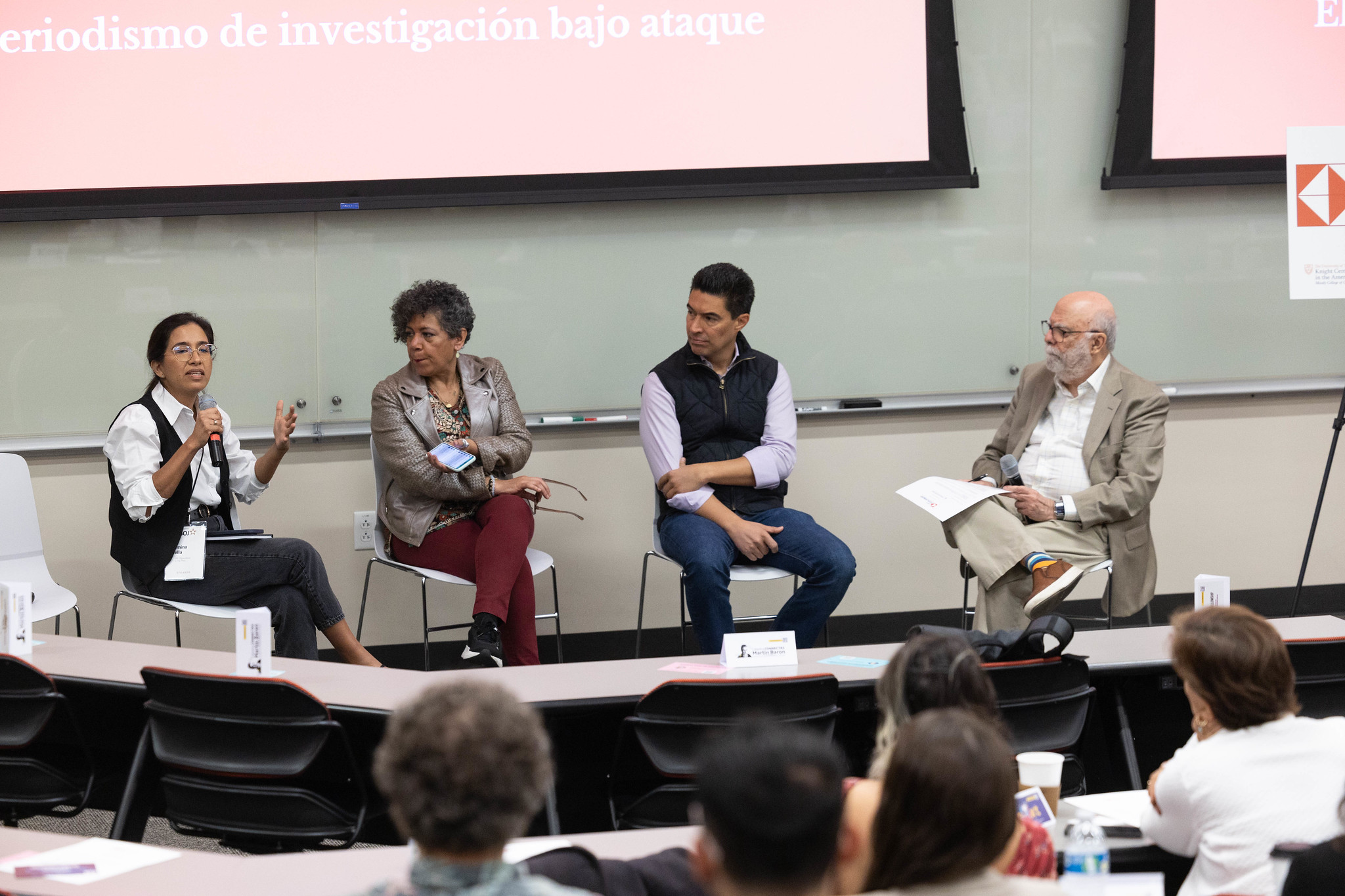

Attacks on the press are undoubtedly one of the main challenges for media and journalists in Latin America. Talking about the state of digital journalism in the region also implies knowing the obstacles to press freedom. Journalists from Guatemala, Peru and Venezuela spoke about these challenges during the 17th Ibero-American Colloquium on Digital Journalism.

With their campaigns against independent media, the governments of several Latin American countries are beginning to threaten press freedom. Can Nicolás Maduro and Daniel Ortega's extreme of media blockages and closures be replicated?

Independent Venezuelan media outlets Efecto Cocuyo and Crónica Uno gave life to Mirador Electoral, a journalistic project that seeks to be a space for discussion on politics and elections before citizens vote on the next president. The initiative is made of TikTok videos, interviews on YouTube and a series of articles.

According to recent research from Ecuador, journalism in Latin America is a profession with invisible psychosocial risk factors, a situation that was aggravated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The main researcher and four journalists explain how to face this reality in daily work.

After an investigation, three Venezuelan journalists realized the best way to help journalism in Venezuela's Amazon region would be through a network that promotes collaboration and produces coverage that is conscious of both the environment and human rights.

The fact-checking coalition C-Informa of Venezuela won the Journalistic Excellence Award of the Inter American Press Association, in its category of data journalism, for revealing the social media disinformation strategy of Nicolás Maduro's regime. Learn more about the winning work in this article.

Following its line of innovation, Venezuelan independent news outlet Efecto Cocuyo launches a collection of NFTs, an element of blockchain technology, to raise funds and denounce the digital censorship suffered in Venezuela. The collection contains 489 images that represent the days that the news outlet has been blocked in their country.

Considering the media crisis in Venezuela, Academia Prodavinci, the educational division of the investigative journalism organization, launched a journalist training program this year. It seeks to train journalists and students in topics such as health, economics and gender inequality in order to contribute to the development of a more solid, contextualized and analytical journalism.

In a panel at UT Austin, four Venezuelan journalists recounted their experiences of persecution and survival during two and a half decades in a country that is no longer a democracy, where print newspapers are lacking and the official media have become hegemonic.
Venezuelan journalist Ronna Rísquez, who specializes in violence and organized crime, spoke with LatAm Journalism Review about the publication of her first book 'El Tren de Aragua: The gang that revolutionized organized crime in Latin America,' about this criminal organization that has a presence throughout the region.