
While other newspapers were cutting children's supplements, the independent la diaria, from Uruguay, launched Gigantes and gained over two thousand subscribers in three years. Their secret? Incorporating children and teenagers into their production processes and addressing topics that truly interest young readers, balancing information and entertainment.

In the midst of election season in Uruguay and ahead of voting for president this October, congressmen from the ruling party propose a bill that penalizes the creation and dissemination of misleading content. Civil society organizations warn that it is not the appropriate solution to disinformation.

Cases of beatings, attacks and insults from fans against journalists have multiplied in many countries in Latin America. Behind the attacks, there may be new codes of conduct among violent fans and a deep intolerance for difference.

A media observatory in Uruguay analyzes news on migration from the most widely read print media in the country. Its researchers say that, in general, the phenomenon is associated with danger and conflict, and that it is not treated in depth by the media. This is due, in part, to the high level of precariousness in which journalists work.

Journalist and researcher of media and digital platforms Daniel Mazzone analyzes the role of journalists in the face of fake news and a digital society. His book "Máquinas de Mentir [Lying machines]" uncovers new work perspectives from within the journalistic community and the structuring of a new contract with society.
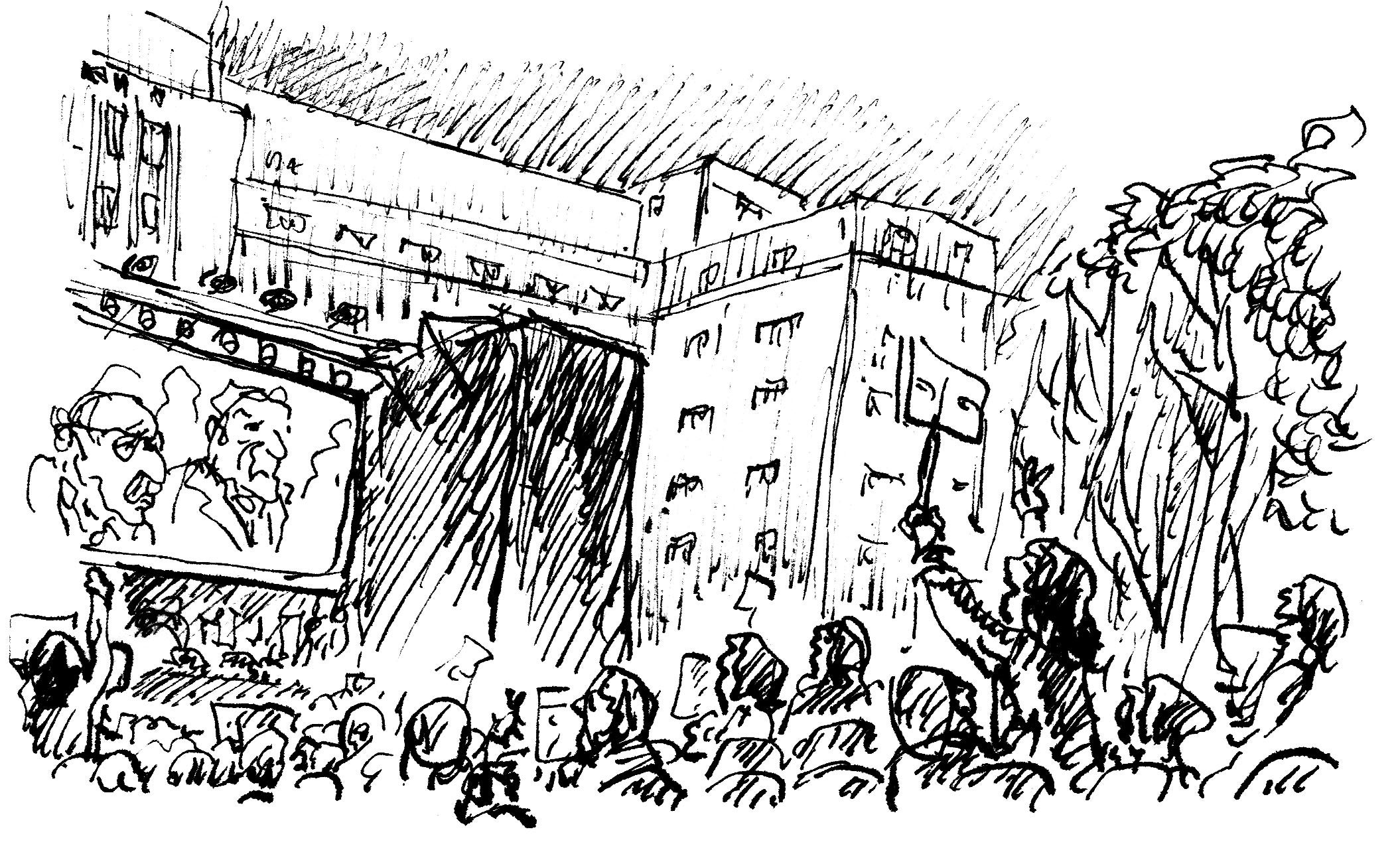
Several decades have passed since the last dictatorial regimes were established in the Southern Cone of Latin America. Human rights defenders and a journalist talk about the challenges of reporting on the recent past, and why it is important to continue doing so.

Alejandro Astesiano was chief of security of the current President of Uruguay, Luis Lacalle Pou, until he was arrested by the Police for leading an organization that falsified documents to obtain passports for Russian citizens. Very quickly, the Uruguayan press obtained the investigative folder of the case which contained more than a thousand Whatsapp chats by the accused.

Inspired by a global trend, media labs are beginning to emerge within news organizations in Latin America to develop innovative journalism-oriented thinking, accelerate the application of technology, seek solutions to problems, and have an impact.

Although Uruguay has been considered a benchmark for freedom of expression, the eighth monitoring report by the Center for Archives and Access to Public Information (Cainfo) recorded a 40 percent increase over the previous year in cases of threats and restrictions on journalists. There has been an increase in the number of cases for the third consecutive year and regressive legal reforms in terms of human rights and freedom of expression.

The most recent edition of the Chapultepec Index of Freedom of Expression and the Press, from the Inter-American Press Association (IAPA), recorded an improvement of 4.2 points on average in the 22 countries evaluated on the continent. The more positive overall picture comes with poor results from three of the largest countries in the region, Argentina, Mexico and Brazil, which lost the most points in the ranking.

Survey of laws and bills that curb and punish disinformation and fake news on the Internet shows growth in Latin American countries. Experts warn of the risk of censorship and self-censorship of journalists.

Between January and June of 2020, Voces del Sur, a Latin American initiative, registered 630 aggressions against the press in the region. These went on the rise or worsened after governments issued a health emergency.