
The research article “Spatial dimensions within hierarchy of influences: How re-conceived notions of space in networked societies impact Latin American journalists” shows that the geographic location of the newsroom influences the perception of the journalistic function.

Over-information, weariness and the need to disconnect. The trend was underway at a global level. It had a pause during the pandemic, when news consumption was essential. Afterwards, global audiences, saturated, seemed to have become overloaded with so much information. Why did many prefer to zap, unplug from the news and take refuge by watching series or opening a book?

The latest report "Journalism, Media and Technology: Trends and Predictions for 2023," published by the Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism, sheds light on what the news industry can expect in 2023. Concerns about the sustainability of some news outlets are on the rise, as are the challenges to innovate.
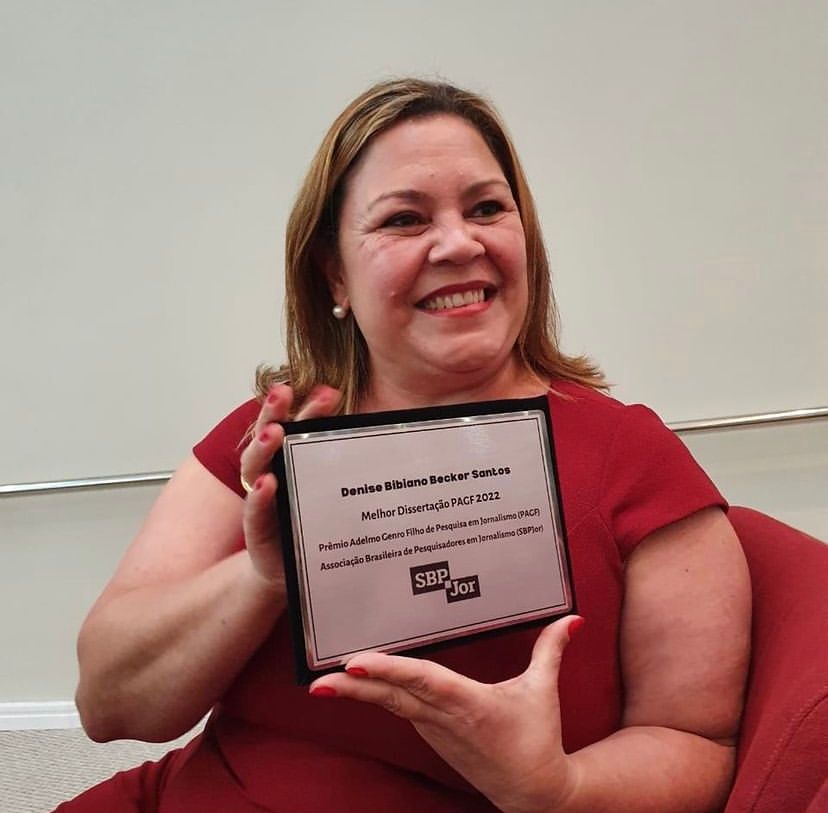

Brazilian researcher Denise Becker, from the Federal University of Santa Catarina, defends transparency as a key value for journalists and news organizations to face the wave of loss of trust that affects the press. Winner of the 2022 best dissertation award from the Brazilian Association of Journalism Researchers, Becker argues that transparency contributes to rebuilding public trust in journalism.

Researchers Summer Harlow, Ryan Wallace and Lourdes Cueva Chacón published on Oct. 7 the research entitled “Digital (In)Security in Latin America: The Dimensions of Social Media Violence against the Press and Journalists’ Coping Strategies.” The study reveals that social media violence needs to be taken as seriously as offline/physical violence.

The survey "Perfil do Jornalista Brasileiro 2021" heard from 7,000 journalists between August and October of last year to draw a current portrait of the journalism profession in Brazil. The final report shows transformations as well as continuities in the journalism scene since the first survey in 2012. Among them is the deepening precariousness of the profession during the last ten years, as shown by low wages, long working hours, and an increase in precarious forms of employment.

Brazil is where a growing aversion to the news is worst, as 54% of Brazilians avoid the news, well above the world average of 38%. In Argentina, 46% now say they avoid news content. The other countries in the region surveyed were Chile (38%), Colombia (38%), Mexico (37%), and Peru (37%).

Journalists, editors and academics from Brazil, India, the United States and the United Kingdom identified that one of the great factors that erodes trust in the news is the way its content works on social and messaging platforms such as Facebook, Google and WhatsApp, on which they have no control over, according to a study by the Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism.

Although the potential of artificial intelligence is vast and the region is hungry for knowledge on the matter, its implementation is still scarce in Latin American media, report says

The FOPEA report, "Situation of Local Journalism in Argentina," found that about 70 percent of the local media in Argentina work mostly with freelancers or commissioned collaborators. FOPEA surveyed 2,464 media outlets and 13,597 journalists from the 23 provinces of the country and the federal district, the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires.
The report, from the Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism, has collected data in four countries: Brazil, India, UK and the U.S.

Researchers looked at 80 news sites from 20 Latin American countries and identified three that stood out in making the audience an active part in making the news: digital natives GK (Ecuador), The Intercept (Brazil) and RED/ACCIÓN (Argentina ). According to the study, published in Brazil Journalism Research, the business model of the three outlets, based on direct revenue from the audience, creates more spaces for collaboration with the public.