
Venezuela has a favorable climate for disinformation and its government has taken advantage of the reach of social media to spread false information. A group of media and digital rights organizations have created the fact-checking network C-Informa to show how disinformation works in that country.

Using satellite imagery and geo-referencing, following the trail of trafficking networks and taking care for the safety of journalist and sources are techniques that journalists Yvette Sierra of Mongabay, Joseph Poliszuk of Armando.Info and freelancer Hyury Potter have applied in their investigations of illegal mining in Latin America.

During the LATAM Festival of Digital Media and Journalism, journalists from Cuba, Guatemala, Mexico, and Venezuela shared how they go around the opacity and hostility of their governments. They agreed that the lack of transparency and access to information can cost human lives.

Venezuela has been subjected to a dismantling of its media ecosystem in recent decades. During the year 2022, at least 95 radio stations have been closed in the country, Zulia state being the most affected. These closures seriously undermine citizens' right to know and the conditions to practice journalism.

Venezuelan cyberactivist and journalist Luis Carlos Díaz showed the power of weaving networks on the Internet when he suffered an enforced disappearance in 2019. In this interview, Díaz talks about his case and explains the situation of the media and journalism in Venezuela today.

All winning stories in this year’s IPYS’s National Journalism Contest were published by independent digital news outlets. This situation remains the same, year after year, due to the Venezuelan government’s censorship. The collaboration and support of international organizations has been key to keeping investigative journalism alive in Venezuela

The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted a silent crisis among journalists: the deterioration of their mental health. In Latin America, ongoing initiatives seek to assess the mental health of journalists. They aim to help them cultivate emotional well-being in an adverse context that, in addition to the pandemic, includes widespread misinformation, as well as violence and hostility against journalists.

Women journalists in Cuba, Venezuela, Nicaragua and El Salvador face misogynistic comments, threats to their physical integrity and their family environment, and violations of their privacy. In this article we learn about the experiences of women who have practiced journalism in these three countries.

A surveillance environment in Venezuela has led to the beginning of doubt against free expression – the beginning of self-censorship. Venezuelan journalists have had to find a way to reinvent themselves between censorship, threats, misinformation and media sanctions.
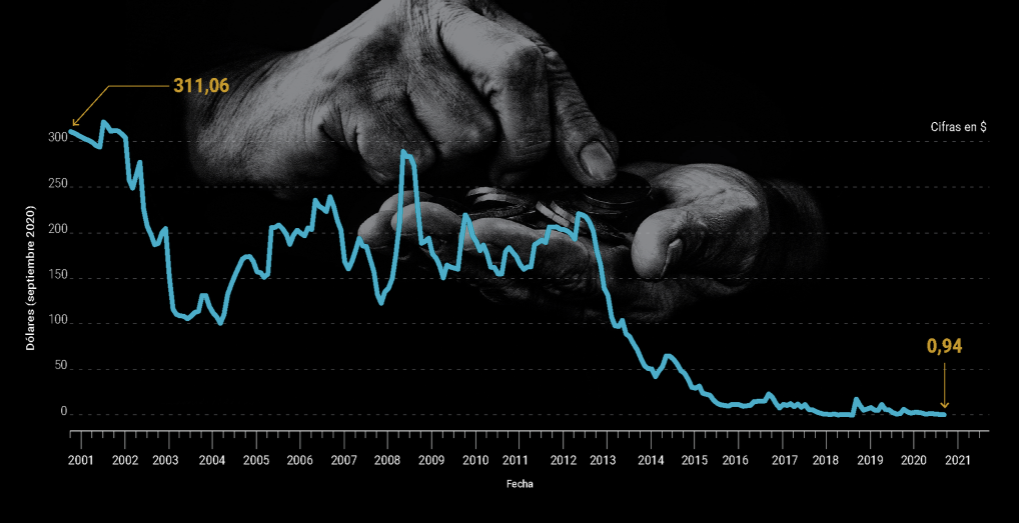
The journalistic multimedia work “La Promesa Rota” (The broken promise) turned opacity and polarization on its head through data collection and analytical work. It created a database that did not previously exist in the country, while at the same time forging a personal bond with readers.

Media accelerator Velocidad shared lessons learned in 16 months of consulting, follow-up and financial support to ten news outlets in Latin America. During this time, these media organizations saw improvements in their organizational structure, audience loyalty, business model and product vision and culture.

Stories about gangs and criminal organizations, border areas with the ambiguity of their limits and jurisdictions, marginal urban towns or a simple central plaza of a city taken over by drug cartels are some of the Latin American topics and scenarios where journalists of the region can find their best reports or a life or death situation.